File size: 5,457 Bytes
1ab1c32 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 |
---
license: mit
arxiv: 2205.12424
datasets:
- code_x_glue_cc_defect_detection
metrics:
- accuracy
- precision
- recall
- f1
- roc_auc
model-index:
- name: VulBERTa MLP
results:
- task:
type: defect-detection
dataset:
name: codexglue-devign
type: codexglue-devign
metrics:
- name: Accuracy
type: Accuracy
value: 64.71
- name: Precision
type: Precision
value: 64.80
- name: Recall
type: Recall
value: 50.76
- name: F1
type: F1
value: 56.93
- name: ROC-AUC
type: ROC-AUC
value: 71.02
pipeline_tag: text-classification
tags:
- devign
- defect detection
- code
---
# VulBERTa MLP Devign
## VulBERTa: Simplified Source Code Pre-Training for Vulnerability Detection
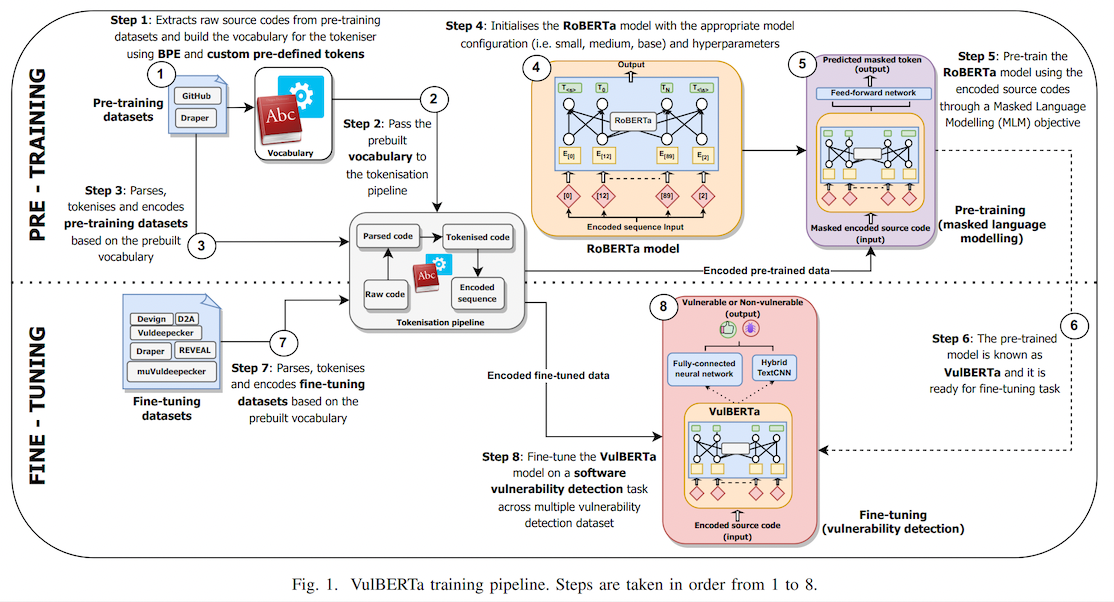
## Overview
This model is the unofficial HuggingFace version of "[VulBERTa](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/tree/main)" with an MLP classification head, trained on CodeXGlue Devign (C code), by Hazim Hanif & Sergio Maffeis (Imperial College London). I simplified the tokenization process by adding the cleaning (comment removal) step to the tokenizer and added the simplified tokenizer to this model repo as an AutoClass.
> This paper presents presents VulBERTa, a deep learning approach to detect security vulnerabilities in source code. Our approach pre-trains a RoBERTa model with a custom tokenisation pipeline on real-world code from open-source C/C++ projects. The model learns a deep knowledge representation of the code syntax and semantics, which we leverage to train vulnerability detection classifiers. We evaluate our approach on binary and multi-class vulnerability detection tasks across several datasets (Vuldeepecker, Draper, REVEAL and muVuldeepecker) and benchmarks (CodeXGLUE and D2A). The evaluation results show that VulBERTa achieves state-of-the-art performance and outperforms existing approaches across different datasets, despite its conceptual simplicity, and limited cost in terms of size of training data and number of model parameters.
## Usage
**You must install libclang for tokenization.**
```bash
pip install libclang
```
Note that due to the custom tokenizer, you must pass `trust_remote_code=True` when instantiating the model.
Example:
```
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline("text-classification", model="claudios/VulBERTa-MLP-Devign", trust_remote_code=True, return_all_scores=True)
pipe("static void filter_mirror_setup(NetFilterState *nf, Error **errp)\n{\n MirrorState *s = FILTER_MIRROR(nf);\n Chardev *chr;\n chr = qemu_chr_find(s->outdev);\n if (chr == NULL) {\n error_set(errp, ERROR_CLASS_DEVICE_NOT_FOUND,\n \"Device '%s' not found\", s->outdev);\n qemu_chr_fe_init(&s->chr_out, chr, errp);")
>> [[{'label': 'LABEL_0', 'score': 0.014685827307403088},
{'label': 'LABEL_1', 'score': 0.985314130783081}]]
```
***
## Data
We provide all data required by VulBERTa.
This includes:
- Tokenizer training data
- Pre-training data
- Fine-tuning data
Please refer to the [data](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/tree/main/data "data") directory for further instructions and details.
## Models
We provide all models pre-trained and fine-tuned by VulBERTa.
This includes:
- Trained tokenisers
- Pre-trained VulBERTa model (core representation knowledge)
- Fine-tuned VulBERTa-MLP and VulBERTa-CNN models
Please refer to the [models](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/tree/main/models "models") directory for further instructions and details.
## How to use
In our project, we uses Jupyterlab notebook to run experiments.
Therefore, we separate each task into different notebook:
- [Pretraining_VulBERTa.ipynb](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/blob/main/Pretraining_VulBERTa.ipynb "Pretraining_VulBERTa.ipynb") - Pre-trains the core VulBERTa knowledge representation model using DrapGH dataset.
- [Finetuning_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/blob/main/Finetuning_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb "Finetuning_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb") - Fine-tunes the VulBERTa-MLP model on a specific vulnerability detection dataset.
- [Evaluation_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/blob/main/Evaluation_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb "Evaluation_VulBERTa-MLP.ipynb") - Evaluates the fine-tuned VulBERTa-MLP models on testing set of a specific vulnerability detection dataset.
- [Finetuning+evaluation_VulBERTa-CNN](https://github.com/ICL-ml4csec/VulBERTa/blob/main/Finetuning%2Bevaluation_VulBERTa-CNN.ipynb "Finetuning+evaluation_VulBERTa-CNN.ipynb") - Fine-tunes VulBERTa-CNN models and evaluates it on a testing set of a specific vulnerability detection dataset.
## Citation
Accepted as conference paper (oral presentation) at the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2022.
Link to paper: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9892280
```bibtex
@INPROCEEDINGS{hanif2022vulberta,
author={Hanif, Hazim and Maffeis, Sergio},
booktitle={2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)},
title={VulBERTa: Simplified Source Code Pre-Training for Vulnerability Detection},
year={2022},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-8},
doi={10.1109/IJCNN55064.2022.9892280}
}
``` |